As part of our project scheduling workshops, hands-on Oracle Primavera P6 or Microsoft Project (MSP) workshops, or scheduling support assignments, we often assist clients with establishing their scheduling best practices. One of the techniques we cover in our EVM training workshops or help incorporate into our client’s scheduling process and procedures is the use of schedule margin as a means to handle schedule risks on a project. The proper use of schedule margin as well as making it a part of a project’s risk and opportunity management process can help to increase the accuracy of an integrated master schedule (IMS) to forecast milestone or project completion dates.
What is Schedule Margin?
The NDIA Planning and Scheduling Excellence Guide (PASEG) Version 4.0 dated August 2019, defines schedule margin as “an optional technique used for insight and management of schedule risks.” Schedule margin is a period of time that is identified in the project’s plan for risk mitigation where an internal target date is set prior to a commitment date such a major project milestone or deliverable. Schedule margin is a defined task in the integrated master schedule (IMS) with logic ties (the immediate predecessor task) to a project finish milestone or intermediate decision point/milestone.
The placement and duration of the schedule margin task is based on a risk management assessment that may include a probabilistic three-point Schedule Risk Assessment (SRA). It may also be driven by schedule incentives, stakeholders needs, subcontractor interfaces, customer provided inputs, tightening of range estimates to single point estimates, or other influences.
Some have described schedule margin as management reserve for time. A simple example would be scheduling your drive to work. Should you easily get through the traffic lights and there are no issues, you can usually make it in 30 minutes. However, because of the “risks” associated with hitting more red lights and other issues, coupled with the penalty of being late, you might plan for the trip to take 45 minutes. Those additional 15 minutes are your schedule margin.
Note however, schedule margin is not a space filler to hide positive float, a schedule stash to cover slippage, or a method used to hold an event’s date. It is a way to incorporate risk into the schedule and improve the forecast accuracy. Some government customers have refined the definition and usage of schedule margin which can impact how you incorporate schedule margin in a given project’s IMS. We will address a couple of specific government customer requirements below.
Applying the Schedule Margin Technique
The customer and contractor project manager both have a vested interest in establishing and using schedule margin. During the development of the project’s requirements definition and planning, the customer will establish need dates. Based on these need dates, target dates for key decision points/milestones are established based on an assessment of risks and constraints. Depending on the complexity, life cycle phase, and risk, the targets may be stated as a single date or range of dates. These targets are provided in the request for proposal or as guidance to the internal project team. The contractor creates a plan and estimate based on their proposal process that includes a risk management assessment. The risks that impact the ability to achieve the target dates are included in the assessment and schedule margin tasks are identified as needed.
Upon award, the contractor creates a baseline IMS with defined schedule margin tasks. These schedule margin tasks are identified as schedule visibility tasks (SVTs) within the IMS. These SVTs are usually placed immediately prior to the decision point/milestone or project finish milestone. The schedule margin SVTs do not have associated resources, they represent a time reserve. Each SVT should be clearly labeled as Schedule Margin and defined. There should be linkage and traceability between the schedule margin SVTs and the risk management plan. The customer may also identify additional schedule margin beyond the contractor’s project target dates to reflect risk to the customer need dates.
As work progresses on the project, the assessment of risks and impact to schedule margin are evaluated. Performance is measured against the baseline targets and forecasts are provided. The risk management plan is also assessed, and mitigations adjusted as needed. These assessments provide input into determining whether the schedule margin requires an updated forecast. Any changes or consumption of the schedule margin should be documented and communicated.
Specific Contracting Requirements
Know your customer’s requirements! Customers may have specific requirements related to the creation, management, and reporting of the IMS. Within the IMS requirements, the customer may have included specific guidance for the use of schedule margin. Be sure you have considered all contract clauses, data item descriptions, and statement of work requirements when planning the project. Views into the Department of Defense (DoD) and Department of Energy (DOE) schedule margin requirements are provided below. Note: we are focusing on schedule margin for this discussion and purposely avoiding other IMS related topics.
Use of Schedule Margin on DoD Contracts
Schedule margin is an optional technique used for insight and management of schedule risks. It is represented by a task or tasks within the IMS with no assigned resources and is established as part of the baseline. In a DoD contractual environment, schedule margin:
- Resides in both the baseline and forecast schedules.
- Should be under the control of the contractor’s project manager.
- Is only placed as the last task before key contractual events, significant logical integration/test milestones, end item deliverables, or contract completion.
- Is associated with schedule risk as part of a formal risk management plan.
The duration of the schedule margin task should be based on risk in subsequent events and traceable to the risk management plan. Schedule margin may be directly or indirectly connected to discrete predecessor and successor activities and fall on critical paths. All schedule margin tasks should be clearly and consistently identifiable. Schedule margin tasks should be excluded (zero duration) when performing a Schedule Risk Assessment (SRA).
Significant changes to the status of schedule margin tasks and impacts to the project’s primary critical path, if any, should be discussed in the Integrated Program Management Report (IPMR) Format 5 or the Integrated Program Management Data and Analysis (IPMDAR) Performance Narrative Report.
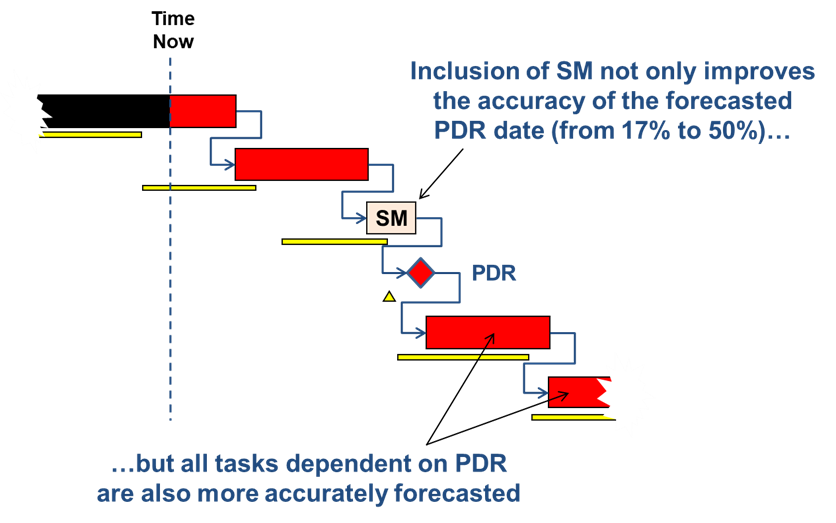
Figure 1 is a conceptual diagram of applying a schedule margin task before the Preliminary Design Review (PDR) milestone.
Use of Schedule Margin on DOE Contracts
The DOE has provided more specific definitions for schedule margin. They have also defined the use of DOE owned schedule contingency to buffer the schedule against unforeseen events that could cause a delay. This is documented in the DOE Guide 413.3-24 for Planning and Scheduling.
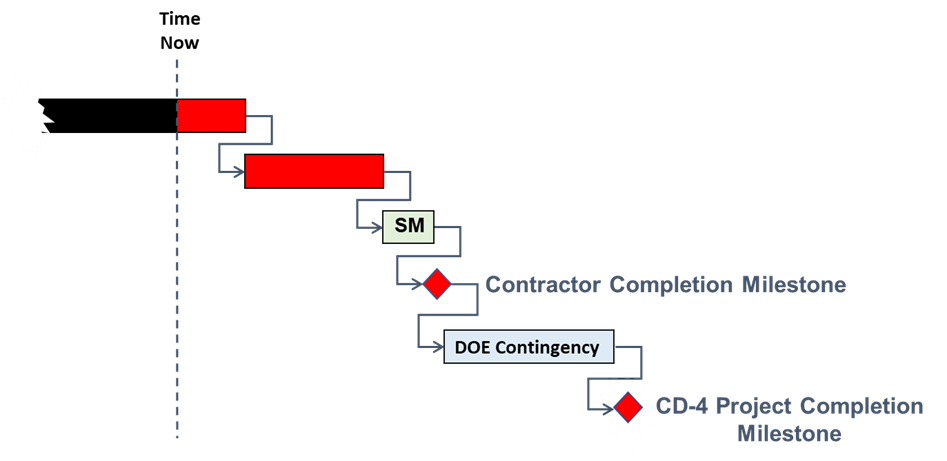
The contractor is responsible for managing their schedule margin. It resides as a single task just prior to the contractor’s project completion milestone. The DOE program office is responsible for managing schedule contingency. Schedule contingency resides after the contractor’s project completion milestone and just prior to the Critical Decision (CD) 4 milestone (Approve Start of Operations or Project Completion).
The contractor’s schedule margin and the DOE schedule contingency are both established in conjunction with CD-2 (Approve Performance Baseline), but updates may occur in conjunction with changes. The schedule margin is set commensurate with the schedule risk calculated at a probability level typically between 70 and 90 percent. The SRA accounts for risk events assigned to the contractor and contractor activity duration uncertainty. Activity duration uncertainty is determined either through a three-point duration estimate or by confidence level (high, medium, or low).
Similar to schedule margin, the DOE owned schedule contingency is set commensurate with the schedule risk calculated at a probability level typically between 70 and 90 percent. This SRA accounts for risk events assigned to DOE and DOE activity duration uncertainty.
The IMS may depict these activities as SVTs. Figure 2 is a conceptual diagram that shows the application of the schedule margin task before the contractor’s completion milestone and the DOE schedule contingency before the project finish milestone.
Interested in incorporating the schedule margin technique into your scheduling best practices? Call us today at (714) 685-1730. We have experienced master schedulers familiar with a variety of scheduling tools that can help you incorporate industry best practices into your scheduling process and procedures. They also well versed in applying schedule risk analysis techniques that complements incorporating schedule margin tasks into an IMS.

Pingback: Schedule Visibility Tasks - Humphreys & Associates