Reviewing Authority Data Call – Not Just a Wish List
Data Call
One of the most important items needed to prepare for an Earned Value Management System (EVMS) review is the data call. This is not just a list of random data; the reviewing authorities have a defined set of data items they want to review so they can evaluate the EVMS implementation and compliance.
Required Artifacts
Over the years the reviewing authorities have fine-tuned the review process and created a very specific list of required artifacts. They use these items to pre-determine the review focus areas so they are prepared to get right to the soft spots in the system and processes.
Formal Review Notification
The process begins when the contractor receives a notification from the reviewing authority that they will conduct a formal review of a project. This could be a Compliance Review (CR); an Integrated Baseline Review (IBR); standard Surveillance; or one of many other reviews conducted to determine the implementation or continued compliance of the EVMS processes and reports. Regardless of the type of review, one of the key items is the data call request. The data call is used to request project information, and could consist of 12 reporting periods, or more, of data. This will vary by agency, type of program, and type of review. In most cases, a minimum of three months of project data will be required; typically, however, 6 to 12 months of data would be requested.
Basic Reports
Some of the basic reports requested are the Contract Performance Reports (CPRs), Integrated Program Management Reports (IPMRs), or similar time phased project performance reports produced from the earned value (EV) cost tool database. The data call request includes the detail source data from the EV cost tool as well as the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) from the beginning of the program. This source data is often delivered electronically to a customer following the IPMR or Integrated Program Management Data and Analysis Report (IPMDAR) Data Item Description (DID) prescribed data formats. The Baseline Logs are often also requested.
Quality Data
It is essential to provide quality data in response to the Review Authority data call. The entire review process can be derailed when data call items are incomplete or inaccurate. Some of the things to consider are:
- Make sure the list of requested items is fully understood (some nomenclature issues could cause an issue).
- The data should be available in the format required in the call.
- Determine the best way to support the data call delivery if it is not specified in the request. The data can be provided using electronic media such as thumb drive, as attachments to emails (the size of the files may prohibit this), or possibly establishing a secure access cloud server to store the data for the reviewing authority to retrieve.
- Contact the requesting reviewing authority to establish a meeting to discuss the data call. This meeting should be used to resolve or clarify any issues regarding the requested information, negotiate potential equivalents of the project data if it does not exactly match the requested information, and establish a method to transmit all data files.
- Develop an internal plan to monitor the progress of data collection. Be sure to have non-project personnel review the data for accuracy and compliance with the specifics in the data call.
- Submit the data call to the requesting authority, follow-up with a phone call or meeting to verify the reviewing authority received the data, can open all the files, and agrees the complete set of data has been provided.
- Follow-up with another call a few weeks before the review to check if the reviewing authority has any issues or problems in evaluating and understanding the data call information. Be willing to work with them until the authority is comfortable with the data.
[NOTE: The number of items on the list depends on (1) the agency conducting the review and on (2) the type of review being conducted. The number of items requested could vary from around 30 to 100 or more.]
Typical Data Call
Some of the basic items typically requested in the data call are:
- Earned Value Management System Description including the matrix of the System Description and related system documentation mapped to the 32 guidelines in the EIA-748 Standard for Earned Value Management Systems as well as to the current version of the reviewing agency’s EVMS Cross Reference Checklist.
- EVMS related policies, processes, procedures, and desktop instructions. Examples include organizing the work, scheduling, budgeting, work authorization, details about earned value techniques and how each is applied, change control, material planning and control, subcontract management, and risk/opportunity management.
- Organization charts down to the Control Account Manager (CAM) level.
- Accounting calendar.
- Project directives including the Statement of Work (SOW) pertaining to Program Management or Statement of Objectives (SOO), EVM clauses, and EVM Contract Data Requirements List (CDRLs) or Subcontract Data Requirements List (SDRLs).
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Index and Dictionary.
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) including budget detail at the CAM level.
- Project and internal work authorization documents.
- Integrated Master Plan (IMP) or milestone dictionary.
- Contract Budget Base Log, Management Reserve Log, and Undistributed Budget Log.
- Risk/opportunity identification and assessments, risk/opportunity management plan.
- Cost performance reports (all applicable formats) or datasets. Provide the reports or dataset in the format provided to the customer such as PDF, Excel, UN/CEFACT XML, or JSON encoded data per the DID on contract such as the CPR, IPMR, or IPMDAR.
- Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) submissions and related native schedule file. This includes the IMS summary report if required.
- IMS Data Dictionary.
- Most recent Contract Funds Status Report (CFSR) or equivalent funding status report.
- Variance Analysis Reports (VARs) or equivalent progress narrative reports as well as the internal and external variance thresholds.
- List of subcontractors including value and type (such as cost reimbursable, firm fixed price, time and materials) including the applicable purchase orders. When EVM requirements are flowed down to the subcontractors, provide a copy of subcontractor EVM related contractual requirements (CDRLs and DIDs).
- Major subcontractor CPRs, IPMRs, or equivalent cost performance reports (all applicable formats) or IPMDAR datasets.
- Major subcontractor IMS submissions.
- Previous audit or surveillance findings, resulting reports, corrective action plans, and resolution and tracking Logs.
- List of specific software toolsets used for accounting, scheduling, cost management, resource management, risk/opportunity management, or performance analysis.
- EVMS Storyboard and flowcharts.
- Chart of accounts, including cost element definition.
- Staffing plans or weekly/monthly labor reports.
- List or copy of contract modifications.
- Cost Accounting Standards (CAS) disclosure statement or equivalent internal corporate procedures.
- Baseline Change Requests.
- Any other data previously provided to the customer as part of a data call.
- Basis of Estimates (BOE) or historical data/productivity rates and efficiency factors.
- Estimate to Complete (ETC) and Estimate at Completion (EAC) documentation.
- Budget reports or control account plans by element of cost (labor hours and dollars, material dollars, and other direct cost dollars) and associated burdens or overhead costs.
- Actual cost reports.
- Open commitment reports.
- Bill of material including cost detail.
- Quantifiable Backup Data for percent complete work packages including MRP/ERP Reports for production work packages.
Reacquaint Yourself
The list includes items that are used frequently, as well as items that are used only at specific times during the project, and will probably be less familiar to the review team. As the collection of the data call items progresses, be sure to establish quick refresher sessions on the less frequently used documents and any other items where the review team might be having difficulty. As part of the process of gathering the data call items, be sure internal reviews are conducted to verify accuracy and traceability, verify the users of the data are familiar with the data content so they can be prepared to answer questions, and current data are available to the review team.
NOTE: This Data Call List is intended for general guidance in preparation for any agency review (e.g., DCMA, DOE, FAA, etc.). For example, in the past, the DCMA Compliance Review Data Call item list contained 102 specific items, but this number varies from review to review and has changed over the years. The number is not as important as the quality of the data items that are delivered to the review authority.
First Impressions
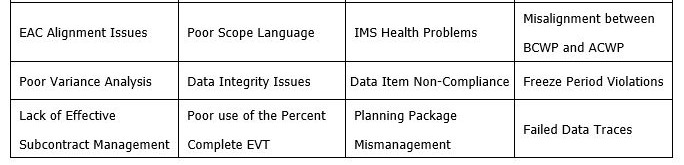
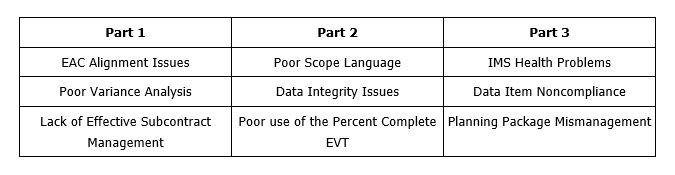
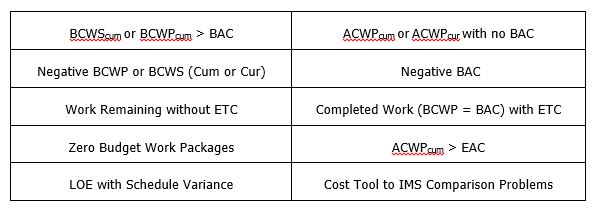
The data call items will provide the first look at the project’s EVM data and process for many of the review team members. The review team members will have the data several weeks prior to the on-site review. They will be performing multiple validation checks using various analytical software tools as well as hands-on analysis of the information. If the data is incomplete, contains errors, and does not trace well, the review team will form a more negative opinion of the EVMS application.
Double Check the Data Call
The data analysis results will be a basis for where attention is focused during the on-site review, as it emphasizes areas that contain anomalies or indicates a lack of system integrity. Significant emphasis should be devoted to the data call items to ensure accuracy and compliance with the review authority’s requests, as it is a very positive way to begin the data call review.
A Humphreys & Associates EVM specialist is always available to answer questions. Give us a call or send an email.
Reviewing Authority Data Call – Not Just a Wish List Read Post »