Contract Performance – Variance Thresholds
Variance Thresholds are an important part of EVMS Variance Analysis. Project managers can use variance thresholds to help identify potential issues with cost and scheduleperformance. By setting these thresholds in advance, project managers can gain visibility into when a cost or schedule variance is trending at a level that needs to be addressed. The goal is to identify issues before they become catastrophic, and while there is still time to correct them before they impact project objectives.
There are a few different ways to set variance thresholds. One common approach is to base them on percentages of expected cost variance over time. This allows project managers to track performance and take corrective action if necessary.
Variance thresholds can be a valuable tool for managing contract performance. By setting these thresholds in advance, project managers can gain visibility into potential issues and take corrective action before they become catastrophic.
Indirect costs can be a tricky topic to navigate, but we’ve got you covered with our in-depth three-part series that breaks down how to determine responsibility for indirect costs.
More EVMS Training
You can now take your EVMS training to the next level with our online course that is based on Humphreys & Associates’ highly regarded three-day workshop. We also offer an extended version of this same program customized for Department Of Defense (DOD) specific requirements, as well one designed specifically toward NASA’s needs!
— Purchase the DOD Course —
EVMS DOD Virtual Learning Lab
— Purchase the DOE Version of this Course —
EVMS DOE Virtual Learning Lab
— Purchase the NASA Version of this Course —
EVMS NASA Virtual Learning Lab
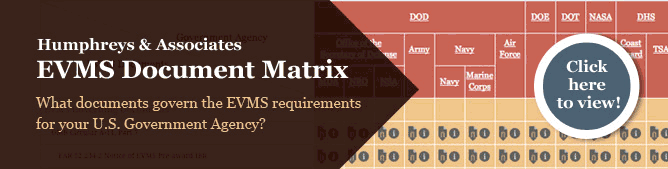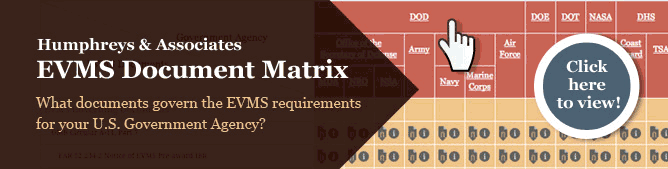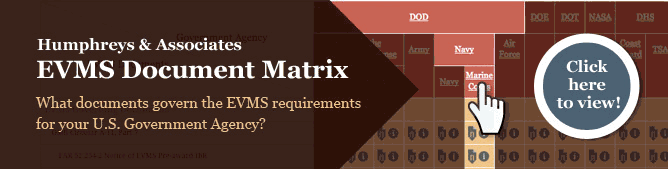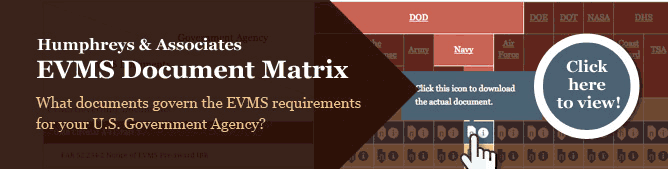
EVMS Document Matrix
Not sure what the different requirements are between the DOE and NASA? Can’t remember if Cost and Software Data Reporting (CSDR) is required for an NSA contract? Check out our easy to read Earned Value Management Systems Document Matrix
All Online Courses
EVM course by Humphreys and Associates will give you the skills needed to manage any project, no matter how big or small. The comprehensive approach covers everything from inception all the way through completion so that students can be confident they’re ready for anything when it comes time take on their next endeavor!
Courses are designed with both beginners in mind but also seasoned professionals who want a refresher or new knowledge update on certain aspects of managing these types of endeavors. You can learn anything from the comfort of your own home with our online self-paced courses. Or if you’re looking for an instructor led experience, we have that too! No matter what time zone or learning style we are suited to accommodate all students’ schedules.
Plus, our instructors are experienced EVM professionals who will guide you through every step of the process, from setting up your EVMS system to closing out your project. With Humphreys and Associates, you can be confident that you’re getting the best EVMS training available.
Our online EVMS courses are affordable and convenient, so you can get the education you need without any hassle. Plus, our courses are designed to help you learn everything you need to know about EVMS in a short amount of time.
Get started today and find the perfect online EVMS course for you.
All Online Courses Available from Humphreys & Associates
Upcoming Public EVMS Workshops
EVM training sessions are offered throughout the year by H&A. EVMS, advanced Earned Value Management techniques, and project scheduling are all covered during these frequent public EVM workshops. These earned value education courses are ideal for anybody wanting to increase their understanding of or application of EVMS or scheduling. Our training programs are suited for individuals with various degrees.
Public EVMS Workshops are offered either in person or online. View our Upcoming EVM Workshop Schedule to find one that best suits your schedule and location.

Contract Performance – Variance Thresholds Read Post »

