Updated December, 2020

Are you confronted with a Stop Work Order and wondering what to do? Stop Work Orders (SWOs), in addition to disrupting contract execution, create much administrative confusion and affect the Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) in the Earned Value Management System (EVMS).
Stop Work Order (SWO)
A SWO is a temporary suspension of work enabling the customer to re-evaluate the contracted work. The customer has a number of reasons to issue a Stop Work Order:
- A change in mission requirements eliminating the need for some or all of the contract scope,
- A need to complete some or all the work scope within funding limitations.
- Advancement in the state-of-the-art that alters the contract requirements.
- Production or engineering breakthroughs that change the current contractual approach.
- Realignment of programs that changes the emphasis on the current contract.
A Stop Work Order could affect the entire contract or could be focused on a specific deliverable item, component, or function. A key concept about Stop Work Orders is that they are temporary. The Federal Acquisition Regulations envision that Stop Work Orders are resolved within 90 days, but allow that the timeframe can be different subject to customer and contractor agreement. The resolution of a Stop Work Order will result in a new contractual direction (a new contractual work order) to:
- Resume the contract (restart the stopped work unchanged);
- Resume the contract with a revised work approach (technical, schedule, and/or cost);
- Delete a portion of the currently stopped work scope (Delete Work Order); or possibly
- Canceling the entire contract (contract termination order).
Stop Work Orders typically result in one or more actions:
- deleting work and its budget from the Contract,
- proposing/negotiating the new course of action,
- implementing the revised approach in the PMB,
- proposing/negotiating a Request for Equitable Adjustment, and or
- preparing a framework for making a Claim against the customer.
Deleting the Work
This article addresses the first of these actions: deleting the work.
Issue Direction
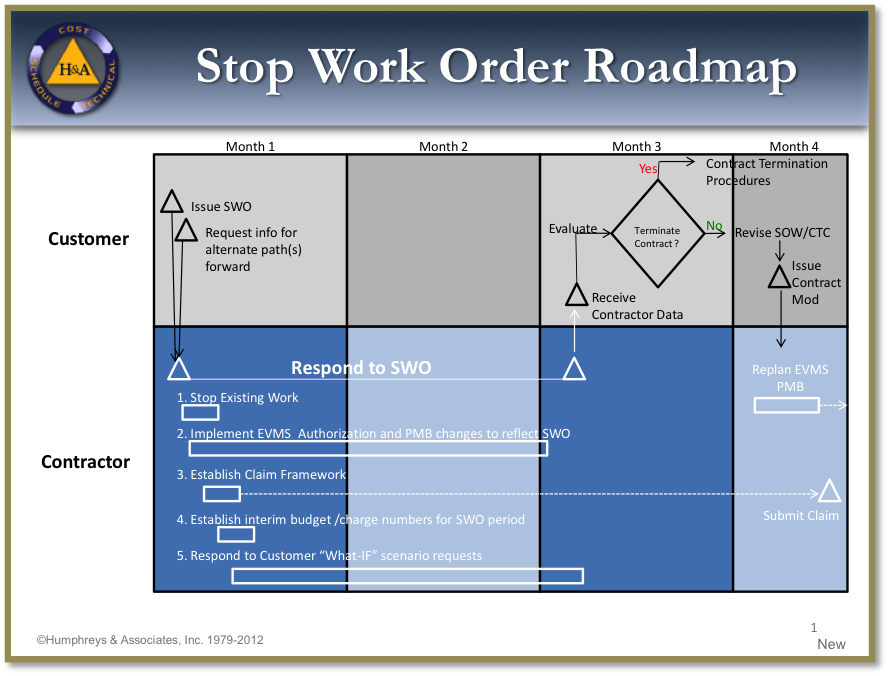
The first step after receiving any Stop Work Order is to issue directions to all affected parties to cease work immediately. Affected parties include Control Account Managers (CAMs), major subcontractors, other team members, and vendors. Your direction should be issued in writing. For CAMs, documents described in the EVM System Description should be used. Typically these documents are revised Work Authorization Documents (WADs) or program directives. For other parties where a subcontract or purchase order exists, the contractor’s authorized representative should issue a formal Stop Work Order (SWO) for the purchase order or subcontract. The SWO process should also provide instructions for the collection of costs related to the stoppage/ delay of work.
Status the Schedule and Earned Value
Inherent in the stoppage of the work is the statusing the schedule and earned value as of the effective date specified in the Stop Work Order. Statusing the schedule and earned value at the Stop Work Order effective date provides the basis for all subsequent actions. If the fiscal period ends within a few days of the Stop Work effective date, it may be reasonable to wait until that date to perform the status exercise (subject to customer approval).
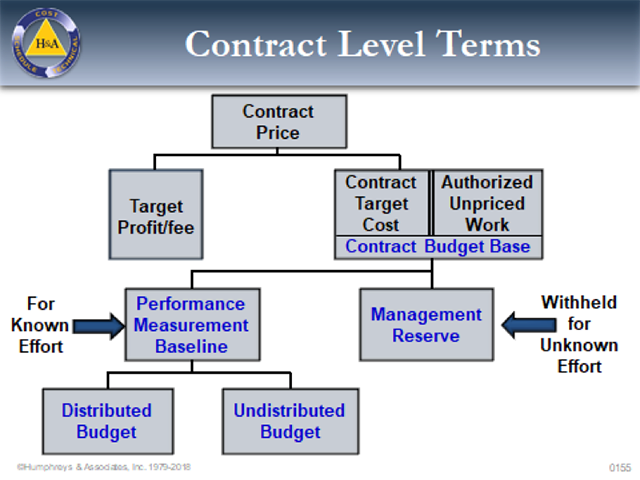
Close the charge number associated with the Work designated by the SWO and Transfer Budgets
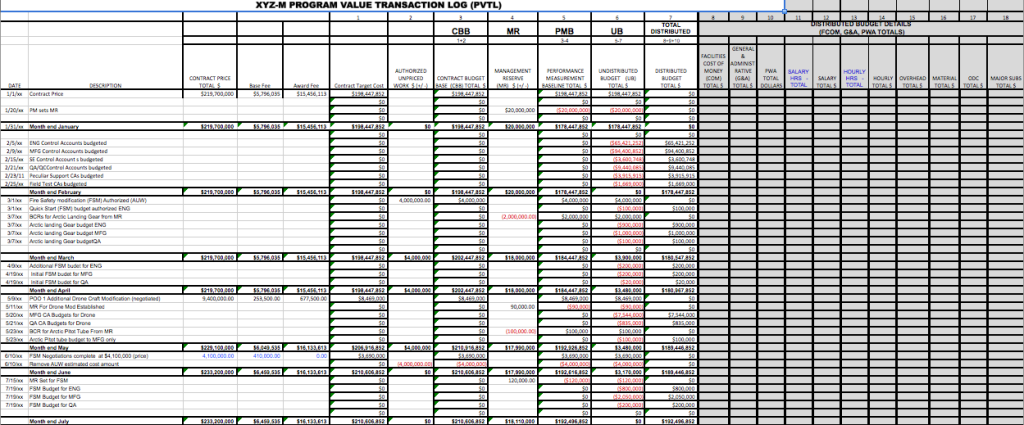
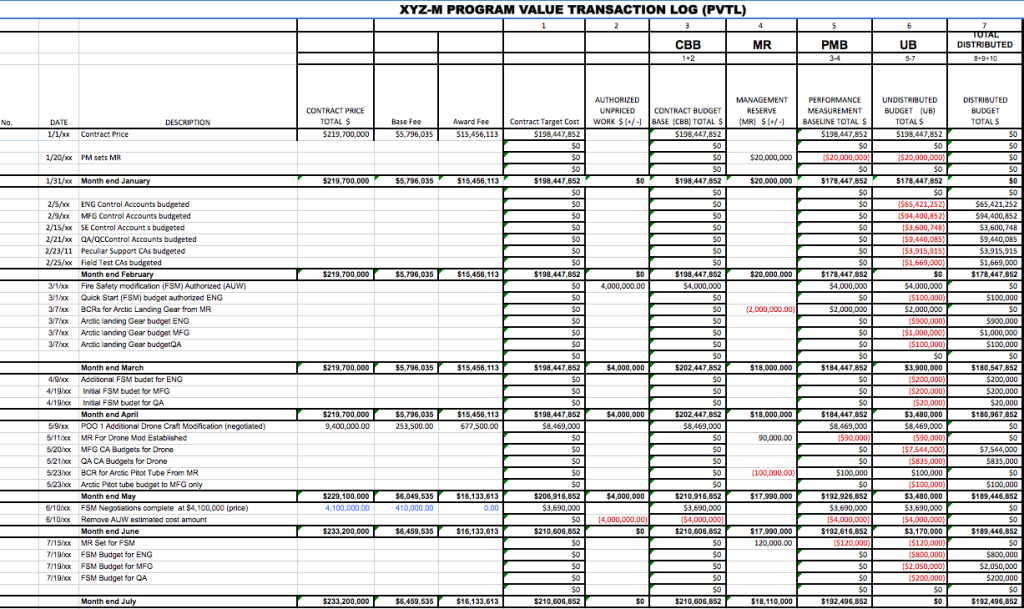
The next step is to close the charge number associated with the work designated by the SWO and transfer associated budgets to Undistributed Budget. Following the company EVMS procedures, Baseline Change Requests (BCRs) must be executed to transfer all Budgeted Cost of Work Remaining (BCWR). Unopened control accounts affected by the Stop Work Order are easy; just transfer the entire amount of the control account budget and its associated Statement of Work (SOW).
Difficulties arise for open control accounts (i.e. work-in-process) or control accounts that are partially affected by the Stop Work Order. Work-in-process control accounts should be closed at the cumulative earned value as of the Stop Work Order date determined in the previous step. [NOTE: In extreme cases where the customer is considering deleting an entire scope of work, the SWO may direct all budget associated with that work scope be transferred to UB for possible subsequent deletion from the contract. In this case, the contractor should include in the Claim framework the capturing of costs for any work already accomplished.]
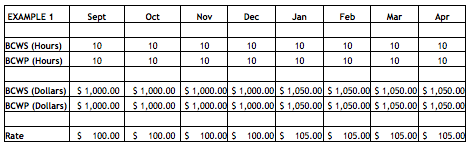
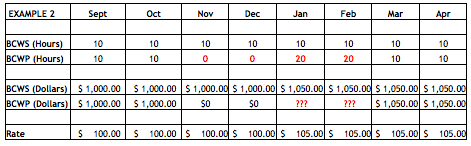
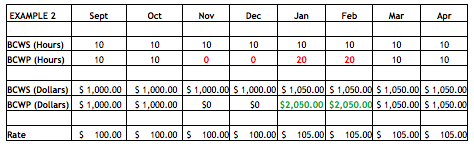
In other words, in order to close any account under normal SWO actions, the Budget at Completion (BAC) and the cumulative Budgeted Cost For Work Scheduled (BCWS) are set equal to the cumulative Budgeted Cost for Work Performed (BCWP). The remaining budget (the BAC prior to closing the control account less the BCWP) should then be transferred to Undistributed Budget. It is important to close the control accounts at the cumulative BCWP value and retain the Cost Variance for the work that is closed.
If the control account were to be closed by setting BAC and cumulative BCWP to either the cumulative Budgeted Cost For Work Scheduled (BCWS) or to the cumulative Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP) where cost variances exist, the BCWR transferred to Undistributed Budget would not be representative of the original work left to be done (understated if an overrun existed; overstated if an underrun existed). Consequently, if the SWO decision were to be “restart the work with no changes”, the budget for distribution to complete the remaining work would also be incorrect, because the close-out was not set to the work that was completed (cumulative BCWP).
Partially Affected Accounts
Control accounts that are partially affected by the Stop Work Order can be handled in one of two ways:
- The first is to close the control account to UB entirely by following the process described above and then issue the remaining scope and budget for the work unaffected by the Stop Work Order to a new control account.
- The second method is to process Baseline Change Requests to remove the BCWR for specific work packages and/or planning packages and leave the control account open for the unaffected work scope. [Unless, of course, the entire contract must stop work until the SWO decision is made.]
Any Summary Level Planning Packages (SLPP) affected by the Stop Work Order should also be closed with scope of work (SOW) and its budget transferred to Undistributed Budget (UB).
All the above work closure actions are to help ensure that no further work is performed on the stopped work (or on the contract, as appropriate).
SWO does not Eliminate Cost Variance
Implementing a Stop Work Order is not an opportunity to wipe out existing cost variances. Contractors and customer program offices often believe that a Stop Work Order presents a great opportunity to wipe the slate clean and start over. In implementing this desire, they set BCWS and BCWP equal to ACWP which erases all cumulative variances. As indicated above, this approach also understates or overstates (i.e., a two-way street) the Budgeted Cost of Work Remaining by the amount of the cost variance that exists at the time. When the time comes to replan the remaining work after the SWO is resolved, there might be too much or too little budget remaining to cover the work because the work was not closed out at the true amount of work accomplished (cumulative BCWP).
The proper approach to deal with the cost variance at the point of the Stop Work Order is to show the variances at the time of the close out of the work, and as necessary, handle the variance issue in the negotiations of the contract modification for the revised work scope or the Request for Equitable Adjustment. Naturally, the contractor wants to erase any unfavorable variances and have the amount added to the Contract Target Cost (CTC)/Negotiated Contract Cost (NCC). Too often the customer succumbs to the contractor’s pleading. The cost variance, however, should continue to exist, and the Contract Target Cost should not be changed for the work scope completed up to the Stop Work Order.
Deleting the Work from the Contract
All the above simply sets the stage for the SWO decision – simply moving the remaining work to UB does NOT delete any work. This article assumes the SWO decision is to delete stopped work, so the customer will typically issue a Delete Work Order (contractual direction of some sort) with instructions to the contractor about what is to be deleted. This could be:
- Delete the remaining work that was not already accomplished;
- Delete ALL the specified scope of work – even if some portion of the work is already done;
- Delete the entire contract (contract termination)
To complete the deletion of work, the contractor would reduce the PMB, UB, and the CBB by the amount specified, thus reducing the Contract Target Cost (CTC) by that amount. The contract itself would be reduced by this CTC amount and the associated profit/ fee for that work.
It is important to follow the customer direction exactly! For example, say the customer is deleting an entire scope of work worth $5Million, but since you already accomplished $2Million worth of that effort, you only put $3Million in UB. When the customer removes the entire scope of work and reduces the CTC (and so the CBB, PMB, and UB) by $5Million, you could end up in a $2Million “Negative UB” condition – which is not allowed under EVMS rules. The proper way to handle this is through the legal Claims process for you to be reimbursed the costs for the work you accomplished (which includes costs for subcontractors and vendors , etc. who will likely be filing Claims against your company). [NOTE: Remember also that under the original contract, you were probably already paid for some portion, if not all, of the accomplished work.] You would also have to store and eventually dispose of items already produced for the customer – that they no longer want. All these should be included in your establishment of a Claims framework.
[NOTE: A Request for Equitable Adjustment (REA) is typically not appropriate for deleted work. This is because the work and budget are no longer on the contract, so there is no budget or schedule to “equitably adjust.” REAs are appropriate for work resumption decisions that will be discussed in Part 2 of this article.]
In summary, make sure you follow these steps to Delete Work when responding to a Stop Work Order:
- Stop the existing work by issuing official written documents.
- Status the schedule and earned value as of the Stop Work Order effective date.
- Execute EVMS procedures to move the scope and the associated Budgeted Cost of Work Remaining (BCWR) from control accounts to Undistributed Budget.
- When the Delete Work Order is received, remove the scope and budget specified by the customer from UB, PMB, CBB, and the CTC as the customer deletes the scope from the contract itself (including associated fee/ profit).
If you have questions on this topic, feel free to contact Humphreys & Associates.