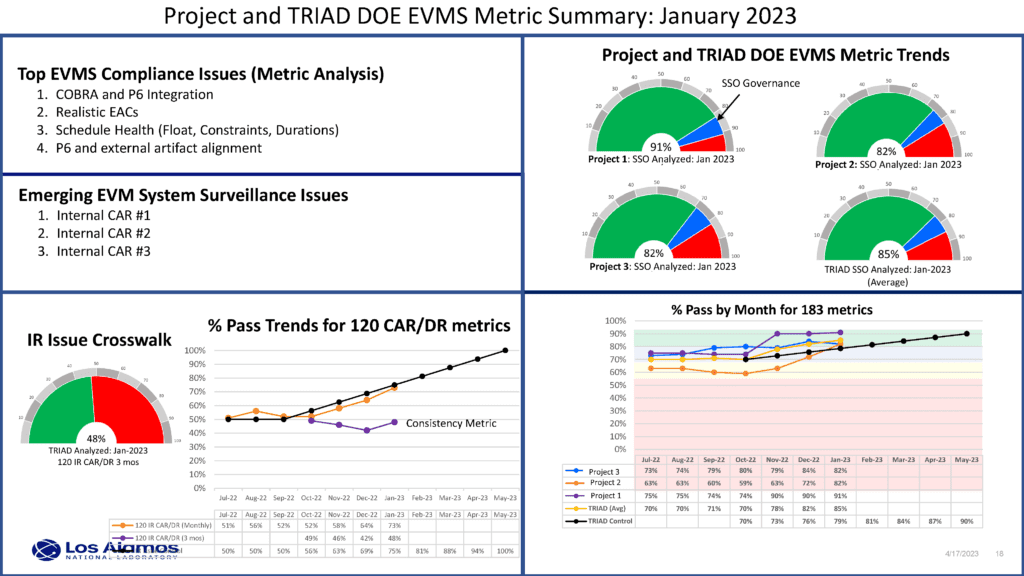
EVM and Unified Risk Management

Working with numerous clients, H&A earned value consultants have observed many instances where project management teams consider the risk and opportunity (R&O) management process to be something technical in nature, run by engineers and focused on the technical aspects of the project’s product. Meanwhile, there is often a separate risk process going on much less formally to consider risks in terms of the project’s schedule and cost goals. This bifurcated approach is a source of risk itself.
Procuring agencies such as the DoD, NASA, DOE, and others have published their own risk management guides. The Government Accountability Office (GAO) has various reports on this topic including examples of their findings. DCMA mentions risk in their Business Practice 4 Guideline Evaluation Template (GET) Process/Implementation Verification Points often used by contractors to check whether their earned value management system (EVMS) meets the intent of the EIA-748 Standard for EVMS guidelines. The exact questions asked by DCMA are important but the overall idea that risk and EVMS are co-dependent is the critical aspect. This is also true for the DOE. They identify risk management as one of the 10 subprocesses necessary for an EVMS.
Setting the Stage
Risk is defined as a factor, element, constraint, or course of action that introduces an uncertainty of outcome that should it occur, could negatively impact the ability to meet the project’s planned technical, schedule, or cost objectives. Negative impacts are sometimes called a threat where the objective is to mitigate the risk. A realized risk becomes an issue that must be resolved to minimize the impact. An opportunity is defined as a positive risk where the objective is to capture the beneficial impacts. Opportunities are not as common as threats.
R&O management is defined as the process of identifying, assessing, and responding to risks and opportunities throughout the project’s life cycle. The goal of R&O management is to identify potential risks and opportunities, determine the likelihood or probability the risk or opportunity will occur, and determine the impact should a risk be realized, or an opportunity is captured. Risks and opportunities are prioritized so that those with greater impact and a higher probability of occurring receive a greater share of resources and attention.
In this blog, we are using the term risk with a focus on the negative impacts or threats to a project.
Example of Common Project Risks and Risk Assessment Approach
H&A’s senior management routinely reviews literature, considers our work with clients, and discusses with our earned value consultants the main contributors to project failure. These findings are updated regularly and presented in H&A training materials as an Ishikawa Fishbone Cause and Effect diagram. Figure 1 is an example of this type of diagram.
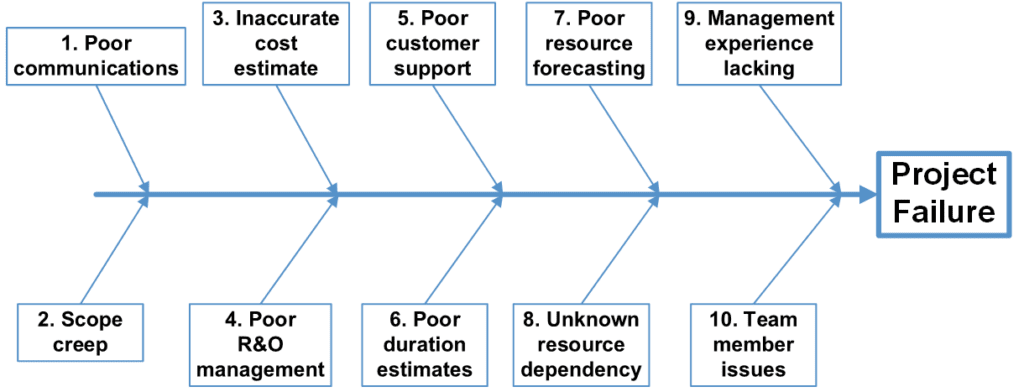
Figure 1: Example of an Ishikawa Fishbone Case and Effect Diagram
When this approach is used for risk assessments, each contributing risk is assessed, and the response documented. An example of a risk/response table is shown below for the first three identified risks.
| Risk Item | Good Example of a Real Project Response to an Identified Risk |
| Poor communications | Goals are known and documented. Communications plan is in place. Have an established cadence for weekly internal and customer meetings to quickly resolve issues. An internal project performance management dashboard is updated daily with current data. Updated IMS and risk register are broadcast weekly to the team. A strong business rhythm has been established. |
| Scope creep | Work scope (requirements and SOW) are well defined and a change control process is in place. Performers are trained in spotting scope creep and how to handle potential changes in scope. |
| Inaccurate cost estimate | Implemented a process enabling cost estimators to search historical actual cost data, identify analogous tasks, substantiate, and document the basis of estimate. For high risk areas, techniques such as the Delphi method, SMEs, and non-advocate reviews are used. Performance is constantly monitored to spot work elements where the actual costs do not align with the budgeted costs or the estimate at completion (EAC) is triggering internal variance at completion (VAC) thresholds. |
This same type of approach can be used by the project control team to create risk Ishikawa diagrams to identify technical risks that could impact the ability to achieve schedule and cost goals. Likewise, risk Ishikawa diagrams can be used to identify risks in the integrated master schedule (IMS) and time phased budget or estimate to complete (ETC) and EAC.
A Unified Approach to Risk
A unified approach includes technical, schedule, cost, and other risk identification and assessment that is an integral part of a contractor’s EVMS. R&O management should be integrated into the EVMS subsystems including work organization, planning and scheduling, work authorization and budgeting, management analysis and reporting, and change management.
Identified risks are analyzed and quantified to develop a risk handling strategy. Where applicable, risk mitigation tasks have been entered into the IMS. Ideally a schedule risk assessment (SRA) has been completed to gain an understanding of duration risks that can help to improve the accuracy of the schedule. Assuming the IMS is resource loaded and leveled, the result is a more accurate time phased budget plan as it incorporates the risk handling strategies when the performance measurement baseline (PMB) is established. The R&O process also provides the necessary rationale for determining the budget amount set aside for management reserve (MR).
The R&O assessments should be a normal part of generating the Variance Analysis Reports (VARs) and updating the ETC and EAC. These assessments can also drive the need for processing baseline change requests (BCRs) as well as determining the best approach for corrective actions.
Using Directed Searches of Identified Risks
To facilitate a unified approach, we recommend establishing a cadence of standing risk review sessions that are conducted in a methodical way to ensure the project manager, integrated product team (IPT) leads, control account managers (CAMs), schedulers, and financial analysts routinely walk through the identified risks that have the potential to impact the project’s IMS or time phased cost.
The intent is to establish a framework such as Ishikawa diagram to guide the risk review session, a directed search of the identified risks should anything further need to be addressed. It is important that a “does anyone have a risk to suggest” approach is not used. Every topic should be covered in every session by walking the Ishikawa risk items. Most of the time it will be a quick “no change” response. Separate Ishikawa diagrams could be used to guide the discussions for the contributing technical, schedule, and cost risks. The meeting room should have the ability to view the live IMS, cost data, and performance analysis data. Team members should be prepared to take notes during the meeting to compile action items.
Figure 2 is an example of a basic Ishikawa diagram of IMS risks the project control team could focus on for the risk review session. This would reflect the project control team’s identified risks to the IMS they routinely monitor.
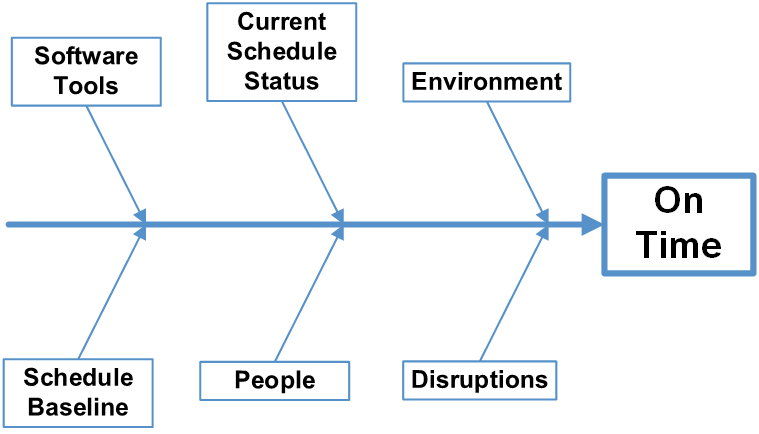
Figure 2: Example of an IMS Ishikawa Fishbone Case and Effect Diagram
For example, updating the current schedule every reporting period has the potential to compromise the integrity of the IMS to provide accurate forecast information about the project’s remaining work. Perhaps the project control team has identified a list of contributing schedule status risks, risk response, and example directed questions for each review meeting. These questions could be focused at the CAM level. The following table is a simple example.
| Risk Item | Risk Response | Example Directed Questions |
| IMS critical or driving paths | Verify logic. Verify traceability exists and has not been damaged by updates. Review constraints, deadlines, and milestones. Perform data quality check, correct errors. | Did milestones move? Did the end date move? What were the baseline dates for starts or finishes that fall into the period?What were the forecasted dates for starts and finishes that fall into the period?What did not happen? Why? |
| Realism | Calculate and assess the Baseline Execution Index (BEI) and Current Execution Index (CEI). Compare the ratio of actual performance to the ratio of future performance. | Is the BEI/CEI result within goals? Are there performance discrepancies? Does the forecast need to be updated to align with reality? Is the forecast showing the performance the team can achieve based on what has been achieved? |
| Quality of ETC/EAC | Verify updates are occurring. Compare current ETC/EAC to previous ETC/EAC. | Has the ETC been updated? What changed and why? For example, for activities with material requirements, price or usage variances may impact the ETC/EAC. For activities with labor requirements, availability or personnel changes may impact future work effort ETC/EAC. |
The same approach would be used for guided budget and cost risk discussions. Tailored cause and effect diagrams should be created for a company business environment and each project’s unique characteristics.
Interested in learning more?
H&A’s training courses purposely include content on R&O management and integrating it into the EVMS. H&A’s Project Scheduling as well as Advanced Earned Value Management Techniques (AEVMT) workshops in particular include more discussion on R&O topics.
A company’s EVMS should be designed to aid the identification and management of risks and opportunities. For example, during the process of developing the schedule and budget baseline, activity durations, resource requirements, and budget distribution can be refined to reflect identified and assessed risks. Proactively identifying and managing risks improves project performance. The expectation of specific risks occurring leads to contingency plans that lower the likelihood and impact of risks as well as the establishment of schedule margin and MR to address identified and assessed risks.
Call us today at (714) 685-1730 to get started.
EVM and Unified Risk Management Read Post »