Establishing a Robust EVMS Self-Governance Process

A previous blog, Benefits of an EVMS Self-Governance Process, discussed why establishing a self-governance or self-surveillance process is important and how an effective process builds confidence with the customer. With a structured and repeatable process in place, effective self-governance demonstrates management’s commitment to maintaining the EVMS and open communications with the government customer. Self-disclosure and quickly addressing EVMS compliance issues are essential.
H&A earned value consultants often assist contractors to implement a robust self-governance process as their level of EVMS maturity increases over time. This blog highlights how H&A provides support and technical expertise to help a DOE contractor to do just that.
Developing the Self-Governance Process and Tools
H&A is a strong teammate in the development and implementation of a robust EVMS self-governance process for TRIAD at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). TRIAD is the prime contractor that provides laboratory management and operations for LANL. H&A is involved in developing tools, refining processes, establishing business rhythms, and summarizing data necessary to support the implementation of a leading-edge EVMS self-surveillance capability. The H&A team is also instrumental in developing the tools necessary to analyze, review, and act on the monthly data set TRIAD provides to the DOE EVMS compliance team.
These tools generate the DOE EVMS compliance metrics (automated and manual) in accordance with the DOE EVMS Metric Specification to ensure TRIAD is able to view the data the same way as their DOE counterparts. Once the tools generate the DOE EVMS compliance metrics, the results are passed to the TRIAD System Surveillance Officers (SSOs) to review and confirm flagged items are either actual fails or exempted/justified based on the rationale captured in the tool. For failed metrics, the SSOs and the project teams use the source data from the tool to identify the root cause and proactively correct EVMS compliance issues. Each month the EVM compliance data is collected across projects, summarized, and graded at the TRIAD level, and then gathered into an EVMS compliance dashboard for TRIAD leadership review and action.
Monthly Self-Surveillance Process
The monthly self-surveillance process includes the following activities.
- For each project, the tool generates the automated metrics from the DOE compliance flat files and then collects the results of manual testing into a single file with all 183 DOE metrics. This tool enables an SSO to review the flags, access the source cost and schedule data, apply exemptions/waivers, and then share the data with the project team to resolve issues. By trending this data across the project’s life cycle and capturing SSO exemptions and monthly actions, the team can analyze the data, determine root causes, address issues, and capture historical EVMS compliance actions in one place.
- An EVMS summarization tool then collects the results from each project and rolls the lower-level results into a summary TRIAD level. Each metric grade (Pass/Fail/Caution) considers weighted EVMS performance across multiple projects to ensure grading is aligned with the exit criteria for the DOE corrective action plans. In addition to TRIAD level grading for each metric, the summary tool also rolls up the metrics to the 10 EVMS Maturity Subprocess areas and 56 Attributes of an EVMS which is documented in the Compliance Assessment Governance (CAG) Appendix to the DOE EVMS Compliance Review Standard Operating Procedure (ECRSOP). This summarization tool provides the subprocess area and attribute grading at both the project and TRIAD levels. By viewing the data across projects and time, the EVMS core team can quickly identify systemic or project level issues.
- A set of tailored EVMS compliance summarization metrics is presented in a “dashboard” configuration for the EVMS core group and senior leadership to review. Leadership uses this summary data to determine where they need to dive deeper into the data and whether TRIAD is meeting their EVMS compliance targets.
Figure 1 illustrates this management level dashboard view.
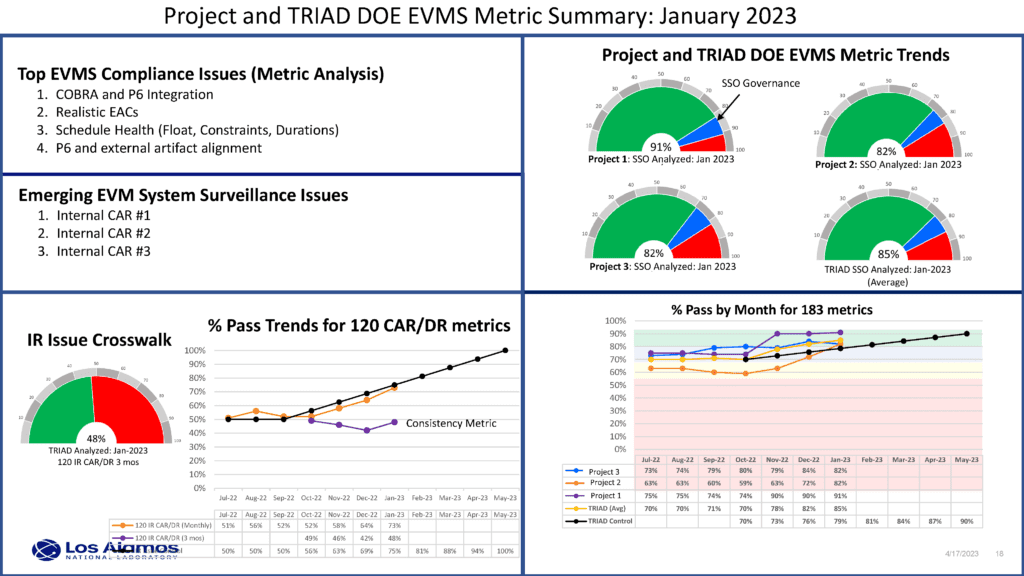
Figure 1: Example of the Summary Level Compliance Metrics Across Projects
- The team also developed and uses a flat file analysis tool that is aligned to the DOE data integrity and quality checks (DIQs). This tool is used for projects transitioning into DOE Critical Decision (CD) Milestones 2 or 3 execution phases that require submittals to the DOE Project Assessment and Reporting System (PARS). This tool ensures the project flat files meet the DOE data quality standards. Like the 183 metrics tool, the flat file tool enables analysts to isolate data quality issues, review the source data, and then determine and track how the team will resolve or justify each issue. In addition to preparing for PARS submittals, these DIQ assessment metrics are also generated monthly to help assess on-going system integration integrity.
Establishing a Best-in-Class Self-Governance Process
In addition to supporting the monthly self-surveillance process, these tools and processes are instrumental in supporting the active surveillance portion of TRIAD’s self-governance efforts. The active surveillance team uses the same tools to summarize and review the “data call” sets in preparation for their reviews. Just like their DOE counterparts, the TRIAD active surveillance team analyzes the 183 DOE compliance metrics to focus their inquiries and document review findings. The H&A team was instrumental in planning, executing, and closing out the recent TRIAD active surveillance that was observed and lauded by the DOE EVMS compliance team.
By supporting the design, development, planning, and execution of all facets of a leading-edge DOE self-governance process, the H&A team helped to ensure our LANL customer has the robust EVMS compliance capability necessary to meet the rigorous DOE EVMS compliance requirements.
As this case study demonstrates, with H&A’s help, TRIAD successfully implemented a structured and repeatable self-governance process with analysis tools that capture objective measures and metrics to actively demonstrate compliance and issue resolution to their customer.
H&A earned value consultants can do the same for you. Call us today at (714) 685-1730 to get started.
Establishing a Robust EVMS Self-Governance Process Read Post »





