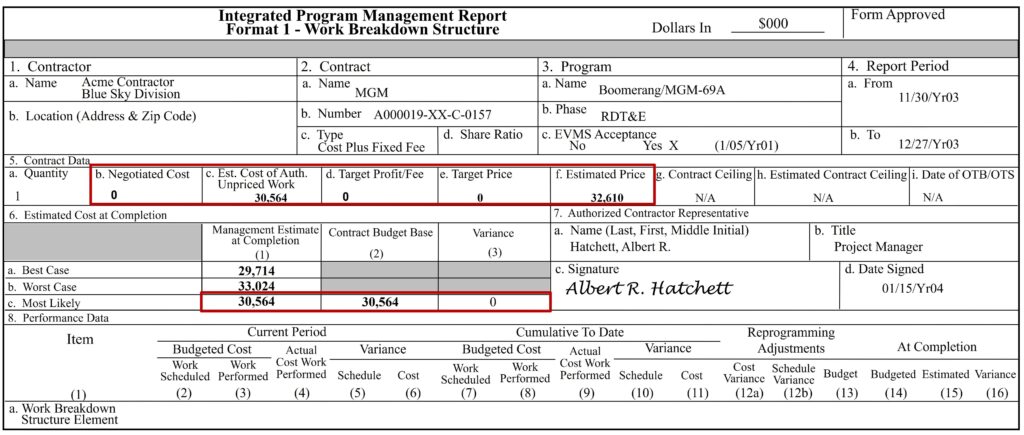
Improving Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) Task Duration Estimates

One of the top reasons projects fail is because of poor task duration estimating for an integrated master schedule (IMS). Without accurate and consistent estimates, project outcomes can become unpredictable, leading to missed deadlines, budget overruns, and overall project failure. A realistic schedule is required to place the necessary resources in the correct timeframe to adequately budget the work as well as to produce credible estimates to complete and to forecast completion dates. While missed deadlines and budget overruns are detrimental for any project, there can be additional business ramifications when producing schedules in an Earned Value Management System (EVMS) contractual environment.
While there are effective methods available to improve task duration estimates, they are often underutilized. A common reason for this oversight is the lack of time allocated to developing the project schedule and determining task durations.
During the proposal phase, initial durations are typically estimated at a more summary level than the detailed execution phase. The proposed work is often defined at a level one to two steps higher than where the actual tasks will be performed. After project initiation, the team’s initial effort is to break the work down into more manageable tasks. This decomposition is crucial for achieving more accurate estimates. It’s no surprise, then, that the initial breakdown efforts often result in duration estimates that don’t align with the proposed durations.
Parkinson’s Law tells us that work expands to fill the time available. If task durations are excessively long, costs will inevitably rise. To counter this, it’s important to require estimators to provide both the estimated effort and the duration needed to accomplish the task. This approach helps to gain a better understanding of the scope of the task and to avoid unrealistic estimates. If you see a task that requires 10,000 hours with a duration of 2 weeks, then you immediately would suspect something is wrong with the estimates.
Techniques for Developing More Accurate Task Duration Estimates
What are your options? H&A earned value consultants and senior master schedulers often employ the following techniques to help a client produce a more realistic IMS.
- Establish a Probability Goal. It is essential to set clear expectations for the estimating team. Without guidance, teams may default to estimates with a 50/50 probability of success, which is a recipe for failure. Instead, directing the team to aim for estimates within a 75% to 80% probability range can lead to better outcomes.
- Break Down Tasks. Decompose tasks into smaller, more manageable components. The further out the task’s horizon, the greater the variability in estimates. For example, asking someone to estimate the drive time from Washington, DC, to Boston without specifying the vehicle, route, limitations, or conditions introduces unnecessary uncertainty.
- Use Professional Judgment. Engage someone with experience in the specific type of work required for the task. A seasoned expert will provide more accurate duration estimates based on their knowledge and experience. Often, we ask the potential task manager to do the estimate, but that person may not be the one with the most related experience or knowledge about the work.
- Leverage Historical Data. If the task or a similar one has been done before, use that historical data to inform the estimate. This approach provides a realistic benchmark for future estimates.
- Use generative AI. If you have access to an AI capability along with access to historical data, that could be an option to leverage the source data using specific prompts to glean relevant information. As with all AI tools, always verify the generated results to ensure it is a useful basis to substantiate the estimate.
- Apply Parametric Estimating. When possible, use parametric analysis to estimate the durations. For example, if it took a specific number of days to clean up a certain amount of toxic waste under similar conditions, this data can be used to estimate the duration of a new but comparable task.
- Engage Multiple Estimators. Gathering estimates from more than one person helps to reduce individual biases and provides a more rounded estimate.
- Apply the Delphi Method. This technique involves three knowledgeable individuals providing estimates or three-point estimates. The initial estimates are analyzed, and the results are shared with the estimators without attributing specific values to any individual. After discussing the findings, the estimators revise their estimates based on the collective insights, leading to a more refined and accurate duration estimate.
- Use Three-Point Estimates. Ask estimators to provide best-case (BC), most likely (ML), and worst-case (WC) durations, along with their reasoning. Applying a formula like the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) duration formula (1BC+4ML+1WC)/6 can yield an adjusted and realistic estimate. You can vary the best and worst case estimate for risk if you have information on that.
To see how this simple approach can work, walk through this exercise. Ask yourself how long it takes you to drive to work most of the time. Let’s say the answer is 45 minutes. Then ask yourself how long it would take on a Sunday morning in the summer when the roads were dry (the best case). Let’s say your answer is 25 minutes. Then ask yourself how long it would take on a Monday morning in the winter during a moderate snow event (the worst case). You tell yourself 90 minutes. Now you have enough information to calculate the PERT duration.
Best Case = 25 minutes
Most likely = 45 minutes
Worst Case = 90 minutes
PERT Duration = (25 + 180 + 90)/6 = 49 minutes
Finally, let’s say you ask yourself how likely it is that you end up on the high side instead of the low side. If your answer is it is much more likely to encounter conditions that slow you down, you would modify the formula to use one and a half times the worst case (25 + 180 + 135)/6 = 57 minutes. That longer duration shows the impact of your impromptu risk analysis and provides a duration that has a much higher probability of being achievable.
Now think about the same scenario but conducted by you interviewing three people who drive the same route to work. That would approximate the Delphi method.
- All or something less. It may not be necessary to analyze every task to the degree suggested. Even if you could do the analysis along the top several critical paths that would be an improvement. If you were to apply numerical factors to the tasks in related portions of the project that would be impactful. For example, all mechanical design tasks or all software development tasks.
What is the best approach?
You will need to analyze your project and determine which approach or approaches would yield useful information at a reasonable cost. If you apply your own thinking on how to improve your duration estimates, you will undoubtedly find a method most suitable for your situation. Depending on a project’s complexity and risk factors, you may also find it useful to take a more formal approach. Conducting a schedule risk assessment (SRA), a probabilistic assessment of a project’s outcome, can help you gain a better understanding of where the duration risk exists in the schedule.
H&A earned value consultants and scheduling subject matter experts often assist clients to establish basic guidance to help scheduling personnel to get into the habit of adequately defining tasks and using techniques to improve duration estimates. This is critical to be able to produce well-constructed and executable schedules to improve the likelihood of achieving project technical, schedule, and cost objectives.
H&A offers a range of project scheduling training workshops that can help schedulers to implement industry best practices. These workshops also cover how to take the next step to implement advanced scheduling techniques such as schedule risk assessments to ensure the schedule is realistic and achievable. H&A earned value consultants and master schedulers often provide one-on-one mentoring using the scheduling tool of choice to help scheduling personnel work through the learning curve of using advanced network scheduling techniques to produce executable schedules.
Improving Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) Task Duration Estimates Read Post »